Watch video recording & Get follow-along PBIX example
If you'd like to try all of this yourself, enter your data below to get immediate access to the PBIX example used in the this tutorial and the full 1-hour video recording of the webinar.
 September 8th
September 8th February 22nd
February 22nd 10 Jul 2025
10 Jul 2025 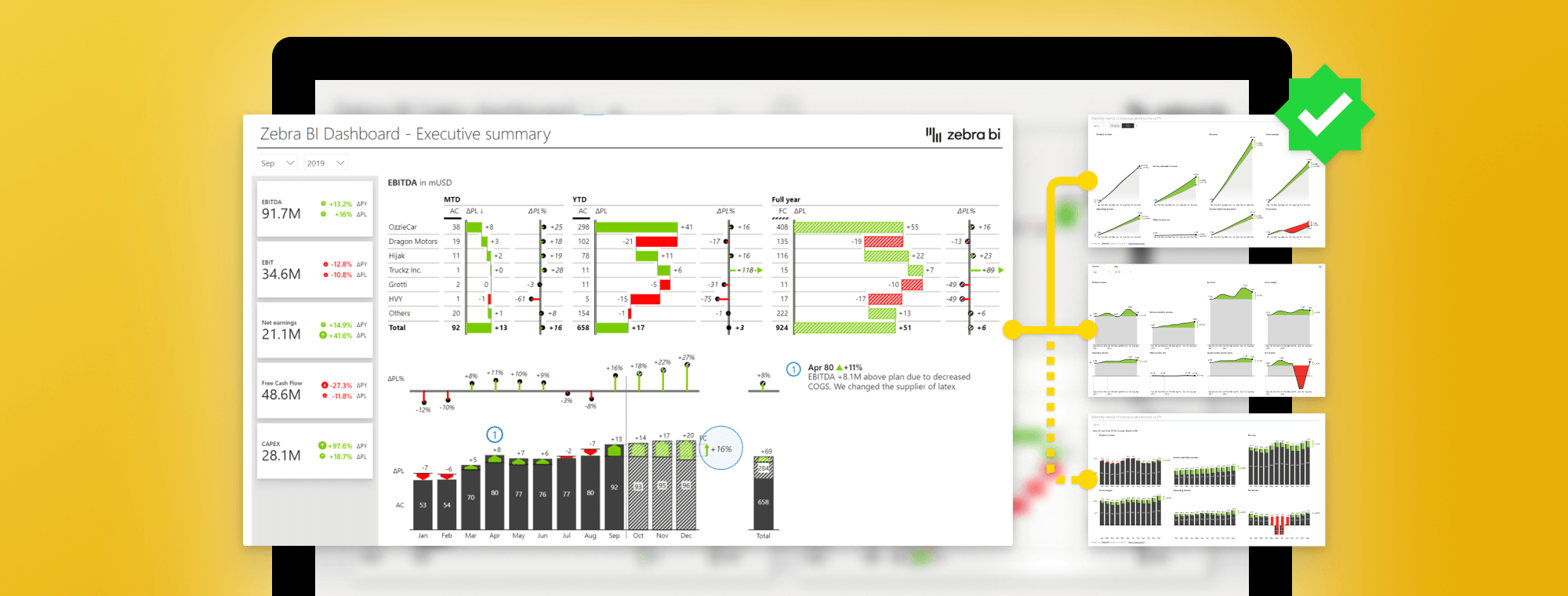
Imagine having a business meeting where you are given puzzles instead of information. To get to the KPI dashboard to round up your business performance, you need to piece the puzzle together. Sounds funny, right? Well, in reality, meetings or preparing a report often consist of pure efforts to obtain and interpret the right data.
In this tutorial, we will look at how to structure actionable dashboards and especially focus on the landing page. We will tell you what to put on the landing page, where to put it, and what tools in Power BI should you use to make those landing pages really actionable and understandable.
Furthermore, just having the data communicating nicely doesn’t necessarily prompt the change you need to improve your business. But what if the clear picture, that also inspires action, is right in front of you the whole time?
The clear and inspiring picture mentioned earlier is what Actionable Reporting is about. It’s not just a fancy phrase, as it centers every decision on data. Moreover, it’s not just about translating data into information but turning data into insights that call for action.
Don’t allow your reports to just describe and summarize the metrics. What is going on, why is it happening, where you may encounter problems, and what are the next steps are the questions your actionable report should cover. The data then becomes a smarter decisions driver, rather than a static element.
Using Actionable Reporting, you won’t just improve the reporting process. Your goal is to ensure minimum action distance. Time spent between obtaining the right piece of information to actually making a decision should be as quick as possible.
Being able to understand and act upon reports rapidly, isn’t just a time and money saver, but an inspiring positive organizational change. For a fresh start, let’s see how to create an actionable KPI dashboard.
One of the things we see most often when it comes to report pages is that people do not make them actionable. They tend to focus on key performance indicators, like total amounts, gross profit margins, cost of goods sold, quantities, and others.
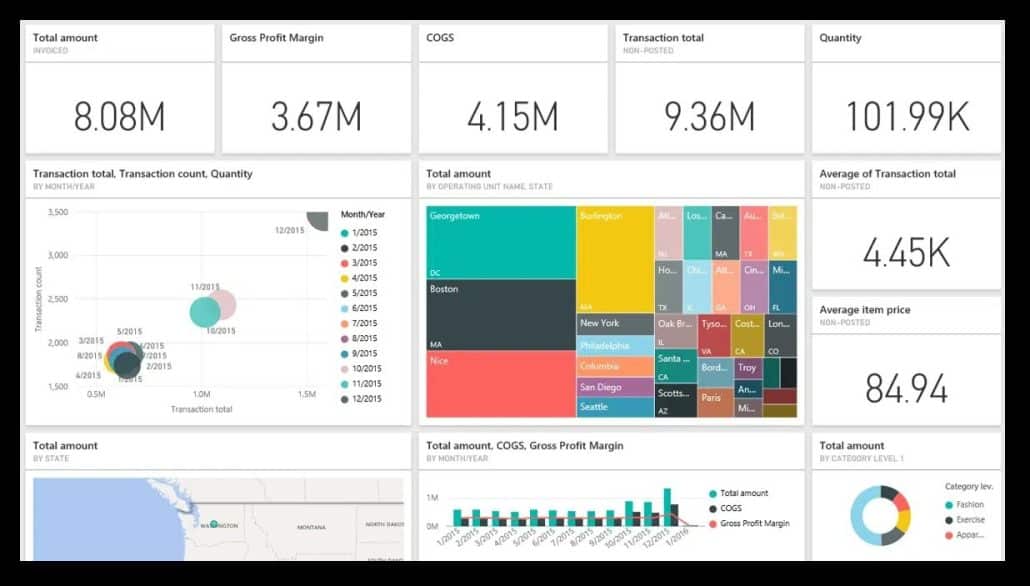
However, just having this information available does not make it actionable. Is the 8 million dollars in sales good or bad? How are you performing against the plan and your previous year? Where do you really need to focus your attention?
In short, this means that this dashboard is not actionable despite showing the most important information. Since there are no comparisons it is impossible to discern any trends or movements. The company with these numbers could be doing extremely well or be on the brink of becoming a failure. The numbers simply tell no story. Learn about the most common mistakes people make when creating dashboards.
Let’s take a look at something a little different.

This dashboard is much more detailed. It has Big Annoying Numbers (trademark pending) at the top so we can see a pattern emerging. It has some interesting charts, like top states, top five employees, and other short charts displaying the top five elements. This is something we recommend you use.
On the right side of this dashboard, there are many filters, which means that I have to click each of them to see what’s going on. However, a dashboard should direct my attention to what matters before I click it.
Examples of "what matters" include:
Let’s look at an example of a sales dashboard.
First of all, it has a KPI area that shows revenues, costs, gross profits, and margins. Instead of just Big Annoying Numbers, each KPI also shows performance versus the previous year and plan. You should put this area on the top left. Why? Because we normally read from left to right and from top down.
This is the KPI area close up:

Now, when the sales manager looks at the KPI dashboard and sees that costs are 5% over budget, they want to see why. So you should set up filtering correctly so when they click on the number, the entire dashboard changes to show just the data for that KPI.
Power BI is great for filtering, you just need to set it up correctly. It allows the user to review information with a minimum number of clicks.
You could also use page tooltips to provide more information without clicking. Regular tooltips just repeat the values, while page tooltips can display additional insights. What really works well is a vertical waterfall chart in a tooltip.

The next idea is to use the drillthrough option, which takes you through to a detailed report on the KPI you are analyzing.

With drillthrough you can guide your user into increasingly more detail, so they can understand individual factors and trends that are shaping the KPI. However, make sure you always provide a way for them to get back to the landing page. This makes for a really user-friendly experience.

Comments are chronically missing from typical dashboards. You could use dynamic comments that are linked to KPIs and specific time periods or business units. Short comments like that provide really useful information to the reader.

The charts located around the KPI area should provide context. In addition to revenue compared with the plan, you could also include the performance of individual product categories and product groups.
Make sure you keep it short. Just show those values that contribute significantly to the final result. You can use the Top N feature to just show the top 5 products, while the others are placed under the Other category.
Also, make sure you provide a help overlay to onboard your end-users. Let them know what your report is about and how they can read it.
To recap, here is the landing page checklist:
Here's an example of a good sales dashboard landing page in Power BI, done with Zebra BI:

Before we dive into different use cases and specific ways to create KPI dashboards, you should know there are three main types of Power BI KPI visuals you can use (and which we will reference later on in this guide as well).
A KPI (Key Performance Indicator) visual is used to display a single, critical metric at a glance. It highlights progress toward a specific goal, making it easy to track performance and identify trends quickly.
A gauge visual represents data in a speedometer-like format, highlighting how close a value is to a predefined target. This category of Power BI KPI dashboard visuals is ideal for showing progress, capacity, or performance within a given range.
A card visual is a simple way to display one key number or piece of information, such as revenue, total sales, or user count. This type of KPI visual in Power BI provides a clean, focused view of important metrics at a glance.
Let’s take a look at an executive KPI dashboard.

Financial executives typically want to see month to date and year to date performance and the full-year performance on the same page and on the same visual so they can compare it.
This is done with the Zebra BI Tables visual and you can always take a more data-focused approach. Our advice, however, is to try to at least visualize the absolute variances in a table, because this is what really guides the reader’s attention.
We wanted to be creative with this one.
The Power BI dashboard below shows the revenue, the weighted pipeline, opportunities, leads, and web sessions. We also included plans and comparisons even though it’s not a financial report. You can still set your strategic goals and benchmarks and include them in your visual.
We also included conversion rates and put them side by side with the pipeline.
Like the other charts we’ve covered, this one also allows you to filter by clicking on the content or drillthrough to more detailed reports.
Find out more about the best tips and methods for building your KPI dashboards.
Every KPI dashboard in every team and every organization is different--two businesses in the same industry may not have the same key performance indicators to track across Digital Marketing Teams, Sales, or Customer Service. And that's fine.
But if you want to narrow it all down to what each department's KPIs should definitely include, it would be this:
Marketing dashboards help measure the effectiveness of campaigns, brand awareness, and customer engagement. Some of the must-have marketing key performance indicators to incorporate in your digital marketing team's KPI dashboard include:
Customer Service KPIs focus on evaluating the quality of support and overall customer satisfaction. Here are some of the essential customer service-related target measures to consider for your key performance indicators dashboard:
Financial Health KPIs are essential for assessing the overall stability and profitability of a business. They provide valuable insights into financial performance and guide strategy for sustainable business growth. Key metrics to include in your financial dashboard and monitor include:
IT Performance KPIs are crucial for evaluating the efficiency, reliability, and innovation within an organization's technology infrastructure. These metrics ensure that IT systems align with business objectives and support overall operational success. Relevant metrics to track when you measure your IT performance include:
Sales performance is a critical driver of business growth and success. Tracking the right KPIs in Power BI allows organizations to measure the effectiveness of their sales strategies and identify areas for improvement. Essential KPIs for the sales performance dashboard include:
As mentioned before, every business and every department is different. But more often than not, measuring the aforementioned KPIs can help you draw valuable insights (and make informed decisions based on them).
If you are looking for advanced Power BI dashboard examples, check out our guide on this (and our list of top 12 most popular dashboards among our customers).
Regardless of which type of Power BI KPI dashboards your organization needs, there are best practices you should keep in mind. Some of the essential ones include:
It's very important to know how to identify the right. It's very important to know how to identify the right KPIs for each of your teams. Tracking the wrong ones could lead to confusion, focusing on the wrong actions, and wasting resources.
Here are some key points to consider when choosing KPIs:
To know which key performance indicators you should focus on, it would help to know the main types of KPIs too (and how to work with them):
Quantitative KPIs are measurable and data-driven, such as revenue, number of customers, or conversion rates. Use these when you need clear, objective metrics to track performance over time.
Qualitative KPIs focus on subjective insights, such as customer satisfaction or employee feedback. These are ideal for understanding experiences and opinions when numbers alone can’t tell the whole story.
Lagging KPIs measure past performance levels, like annual revenue or completed projects. Use these to evaluate results and determine if goals were met.
Leading KPIs predict future performance, such as website traffic or sales inquiries. Use these to identify trends early and make proactive, data-driven decisions.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) are tools for performance management, very similar in nature, but serving different purposes.
KPIs are specific metrics like customer retention or net profit, used to track ongoing activities and progress toward benchmarks.
OKRs, however, are goal-setting frameworks with qualitative objectives and measurable key results, designed to align efforts and drive ambitious, time-bound outcomes. While KPIs focus on maintaining and improving processes, OKRs encourage innovation and strategic growth. Together, they balance current performance with future goals.
Once KPIs are defined, regularly monitoring them is essential to track performance and make data-driven decisions. Use dashboards or tracking tools to visualize trends and patterns in real time. Establish a routine for reviewing KPIs, whether it's weekly or monthly, and adjust strategies as needed to stay on track.
Looking at actual performance against targets on a regular basis will help your strategic decision-making and help you better align your KPIs with business objectives. Plus, the more often you check for your metrics, the sooner you can identify problems across the board, like
Make sure every member of your company knows how to monitor their individual and team performance indicators in Power BI (our can come in handy here, as you don't need to be a Power BI expert to analyze the dashboards you create with Power BI and Zebra BI).
Advanced DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) allows you to unlock powerful insights from your data, especially in tools like Power BI. By using complex formulas and calculations, you can create dynamic measures, analyze trends, and perform detailed comparisons. Mastering DAX enables deeper, more actionable data analysis.
The good news is Zebra BI can handle a lot of the heavy lifting for you, so you don't have to waste time coding DAX from scratch. With Zebra BI, you can easily create advanced visual representations and calculations, even if you're not an expert in DAX. This allows you to focus on the analysis and actionable insights rather than spending time figuring out complex DAX functions.
Power BI templates can save time and ensure consistency when working on reports or dashboards. Leverage pre-built dashboard templates for visualizations, presentations, and analysis frameworks to streamline your workflow. Customizing KPI templates to fit your specific needs can also improve efficiency and professionalism.
Have you checked our collection of Power BI templates, by the way?
When implementing best practices, it's also important to learn from mistakes. Here are common pitfalls to avoid when using Power BI:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are meant to focus on what truly matters for your business or project. However, not all KPIs are created equal. Choosing the wrong KPIs — ones that don’t align with your strategic goals — can waste time and resources. When selecting KPIs, ensure they are tied directly to your organization's objectives and measurable outcomes. Focus on metrics that genuinely drive success rather than tracking data for the sake of it.
KPIs need to be clear and specific to be effective. Vague KPIs like "improve customer satisfaction" without defining how you’ll measure it can lead to confusion and lack of accountability. Instead, aim for measurable targets such as "increase customer satisfaction score by 10% within six months." This provides clarity and helps everyone understand what success looks like.
Setting ambitious goals is important, but unrealistic KPI targets can demotivate your team and lead to burnout. It's crucial to set achievable, data-driven goals based on historical performance, market conditions, and available resources. Realistic targets inspire progress, while impossible ones can hinder morale and lead to frustration.
KPIs are only effective if someone is responsible for tracking and achieving them. Without designated ownership, they can easily fall by the wayside. Assign clear accountability for each KPI to specific team members or departments. This ensures there’s someone actively driving progress and reporting on results.
Tracking KPIs is only half the battle. If the insights gained aren’t used to drive decision-making and improvements, they lose their value. Regularly review your KPIs, identify trends, and take action where needed. Use the data to adjust strategies, allocate resources, or improve processes to ensure you’re making meaningful progress.
Presenting KPI data in overly complex visuals can confuse stakeholders and obscure critical, otherwise actionable insights. Avoid cluttered graphs, excessive data points, or unclear labels. Instead, use simple and intuitive custom visuals that highlight key trends and results. The goal is to make it easy for your audience to understand performance at a glance.
Fortunately, Power BI provides powerful tools to create interactive and visually appealing KPI visuals, enabling you to quickly analyze data and make informed decisions.
Let's walk through the steps to create effective KPI visuals in Power BI:
Organizing and cleaning your data is a critical step to ensure accuracy and reliability in your analysis (as well as gaining actionable insights from it, of course).
Here’s how you can do it effectively:
In one of our webinars, Tilen and Mark (Lead BI Specialists) went through how to create a star schema data model and how to use advanced visualizations to make the numbers make sense (and quickly, to everyone in the organization). Their demo is largely based on financial dashboards, but here it is, in case you want to learn more about creating actionable dashboards in Power BI.
Choose charts, graphs, or table visualizations that best represent your data and help all stakeholders drive actionable insights. Ensure they are clear, concise, and easy to interpret. Here are some examples of Zebra BI visuals you can easily incorporate with your data model to relay your numbers in a clear, concise, and impactful manner:
By the way, here's a quick guide on how to add definitions to your KPIs in Power BI with Zebra BI, so you can ensure that all stakeholders have a clear understanding of the data being presented.
When designing a dashboard, start with a really good landing page. This is the first page your users will see, and it sets the "tone" for finding actionable insights.
When designing it, keep your audience in mind and personalize it for them. A sales manager (and their sales team) will need a sales KPI report with all the metrics they're responsible with. It could be about revenue targets, conversion rates, or other measurable goals agreed on.
How do you come up with the right KPIs? The best way is to talk to the users and then think about what contributes to these KPIs (and how they help with your business' strategic goals). Then you might focus on a breakdown by business units, by account managers or something else.
You really should make the landing page a priority. A good landing page drives adoption and user engagement. If you do a good job with the landing page, then people will keep coming back to their dashboards.
Once you have the landing page, you need to make sure that people will be able to navigate from the landing page to detailed reports. If possible, have it available just a click away. Do not make users click a series of filters or slicers on the landing page. That’s not what it’s there for. The landing page should provide key information and links to other reports.
Make navigation available through the content. When a user wants to investigate a certain data point, the most natural thing is to click on the element. This is where you should use the drillthrough option in Power BI.
With drillthrough you can easily move the user from the landing page to a report that is automatically filtered based on the choice the user just made. From there, they can navigate through multiple pages and then return back to the landing page.
Our next stop is a Power BI dashboard with the ever-popular speedometers.

Individual charts are showing gaps but they’re not scaled. If you look at the two yellow charts, the one showing a larger gap is actually working with much lower totals, so it is probably less important than the other one.
Each chart is a different color and it’s impossible to see what individual colors mean if anything.
It is possible to do better. Here is a Power BI dashboard example for an actionable executive board.

This dashboard has a KPI area showing key information about EBITDA in EBIT, net earnings, free cash flow, and CAPEX. You can click individual KPIs to filter the page and show information to date as well as forecasts and plans.
Or you could click on the free cash flow KPI that’s red and probably needs your attention. A click applies a new filter to show details about the problem area.

You can also drill through individual charts to locate the actual issue for poor results.

This makes it much easier to get the information you need to take action.
Before you can visualize your KPIs in one place, your KPIs should be consolidated. Learn how to consolidate your KPIs using 3 hyper-effective ways.
Visualizing KPIs in Power BI is quite a challenge. Natively, you don't have a lot of good options to visualize the performance of your KPIs cards in Power BI.
We came up with a solution for this, though.
The KPI area in this example was created using the Zebra BI Cards visuals, which helps bring your Power BI KPI cards to a whole new level. This interactive visual was created in response to our users’ requests.
Made you curious?
Try Zebra BI for Power BI, now.
Outstanding article. Most articles on the internet talk about things only at a concept level. This is something that can be used immediately. Too good. Keep up the good work.
Thank you Bhushan for your feedback. 🙂 If you are not already using our visuals you can try it out for 30 days for free or if you do, we would appreciate if you will give us your review on AppSource. Thank you. 🙂
Big Annoying Numbers (trademark pending)