What is EBITDA, how to calculate EBITDA, and how to present it
Embarking on a journey to understand a company's financial health? One essential metric is EBITDA. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into what EBITDA is, unravel the steps on how to calculate it and explore how to effectively present it. No matter if you're a budding entrepreneur, an investor, a finance professional, or an interested individual, this guide is crafted to enhance your financial literacy and analytical acumen.
This comprehensive guide unravels the concept of EBITDA, an acronym for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. You'll learn why it serves as a valuable alternative to net income for assessing profitability and operating efficiency. We'll delve into the different methods of calculating EBITDA from financial statements, ensuring you understand each approach. Finally, we'll explore various ways of presenting EBITDA, including how to incorporate it into your financial statements. We'll also utilize it for business valuation and benchmarking.
With a firm grasp of EBITDA, you'll be better equipped to analyze and understand a company's financial health, whether you're making investment decisions, assessing business performance, or considering an acquisition. So, let's get started and master the ins and outs of EBITDA.
Want to skip all the fuss and present EBITDA like a pro?
Kickstart your journey to professional financial presentations with Zebra BI for Office, your companion in mastering EBITDA.
Zebra BI was made for:
- BI specialists
- FP&A specialists
- Consultants
- Digital transformation officers
- C-level and managers
Understanding EBITDA
EBITDA is a pivotal financial metric that provides an alternative perspective on company profitability. Its true strength lies in its ability to reflect the financial outcome of core operational activities, as it excludes certain non-operational elements that could cloud the picture of a company's genuine performance.
Investors, financial professionals, and analysts often use EBITDA for an unbiased view of company profitability. By filtering out non-cash expenses like depreciation and amortization, as well as factors affected by a capital structure like interest and taxes, EBITDA can highlight the cash profits a company generates from its operations.
While EBITDA doesn't fall under the umbrella of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), it has found wide acceptance among publicly traded companies. They often present EBITDA figures in their quarterly reports, thereby offering an added layer of understanding into their operational profitability. Alongside the standard EBITDA, these reports might also include adjusted EBITDA numbers, which further exclude expenses that don't routinely affect the company's cash flow.
EBITDA, therefore, shines a light on a company's ability to generate profits from its core business activities, uninfluenced by factors like financing decisions, accounting practices, or tax regulations. Its all-encompassing nature and ability to reveal a company's inherent profitability make EBITDA an essential instrument in the financial analysis toolkit.
Calculating EBITDA
Calculating EBITDA is a crucial step in analyzing operational profitability. There are several methods to calculate EBITDA, each providing the same outcome through different paths. The following sections will guide you on how to calculate EBITDA using these methods.
Top-line-down Method
This method begins with the company's net sales and subtracts the cost of goods sold (COGS) and operating expenses, excluding depreciation and amortization. Here's the formula:
EBITDA = Net Sales – COGS + Other Operating Income – Operating Expenses – Other Operating Expenses (excluding Depreciation and Amortization)
Bottom line-up Method
Starting with net income, this method adds back taxes, financial income, depreciation, and amortization, and subtracts financial expenses. The formula is:
EBITDA = Net Income + Taxes + Financial Income – Financial Expenses + Depreciation and Amortization
The shortest way
This is the most straightforward method and involves adding depreciation and amortization back to operating income. The formula is:
EBITDA = Operating Income + Depreciation and Amortization
Each method of calculating EBITDA leads to the same outcome but approaches it from a different angle. The figures necessary for these calculations can be found in company financial statements. The earnings (net income), tax, and interest figures are usually shown on the income statement, while the depreciation and amortization figures can often be found in the notes to operating profit or on the cash flow statement.
Knowing how to calculate EBITDA from financial statements is crucial for anyone looking to dig into a company's financial health and operational profitability. It provides insights beyond traditional net income calculations, helping users make more informed and strategic business decisions.
Presenting EBITDA
Once you have calculated EBITDA, the next step is to present this data in a meaningful way that allows you and other stakeholders to gain valuable insights into the company's operational profitability. Here's how to present EBITDA:
In the Financial Statements
EBITDA can be included in your financial statements, such as income statements, alongside other key financial figures. If you're using Excel or Zebra BI, you can easily incorporate an EBITDA calculation formula into your spreadsheet. This allows for seamless EBITDA integration into your financial analysis and reporting process.
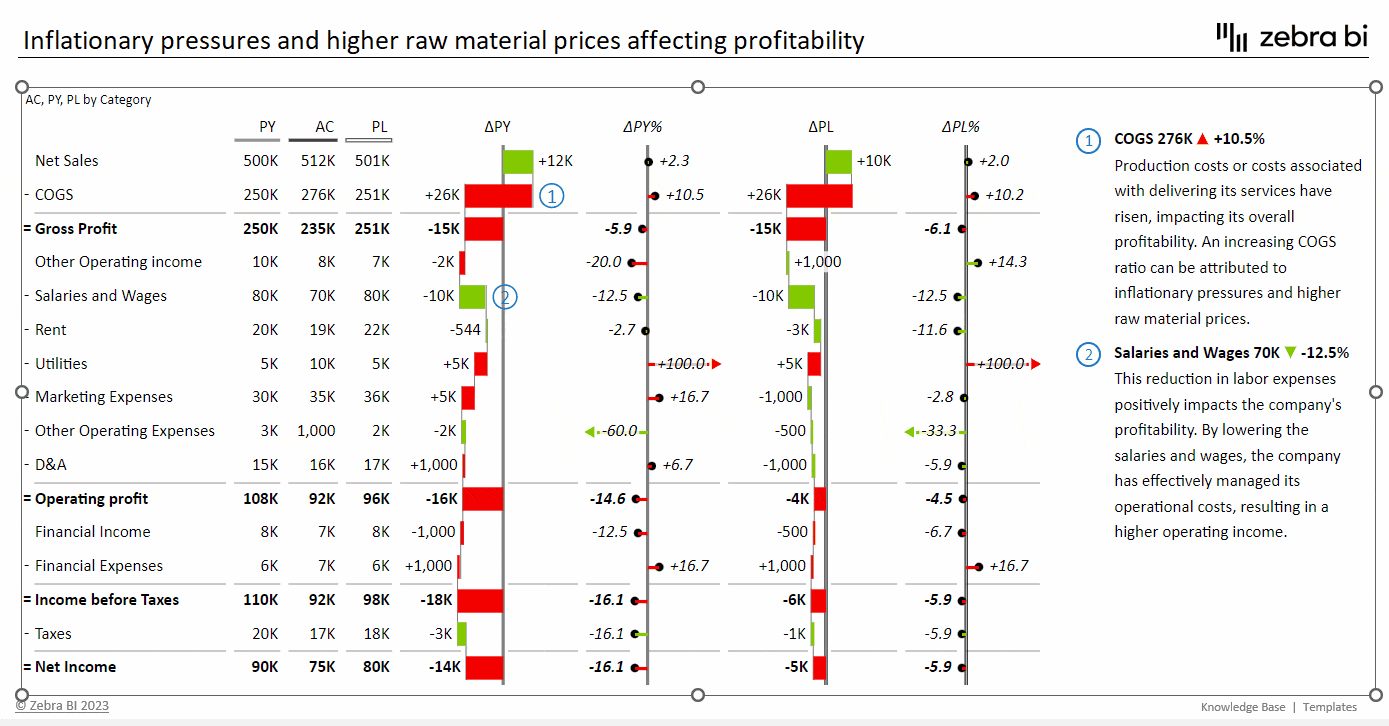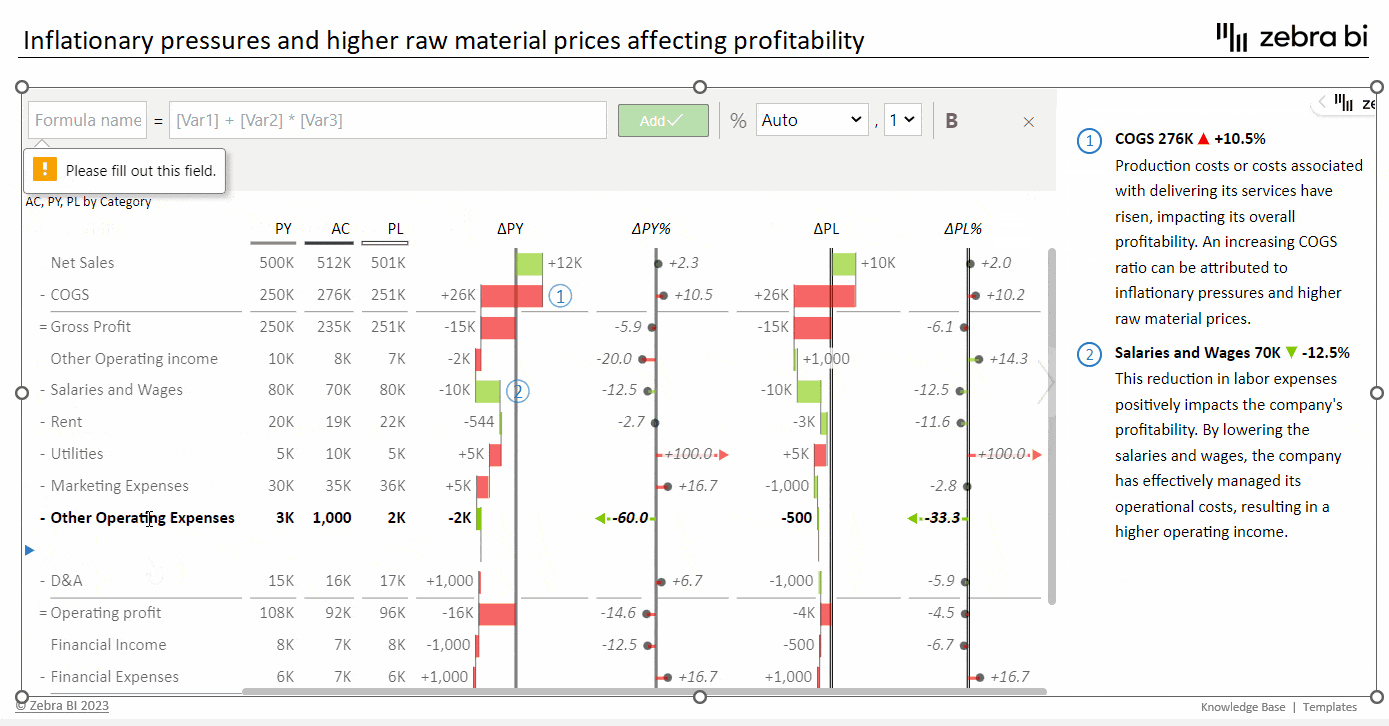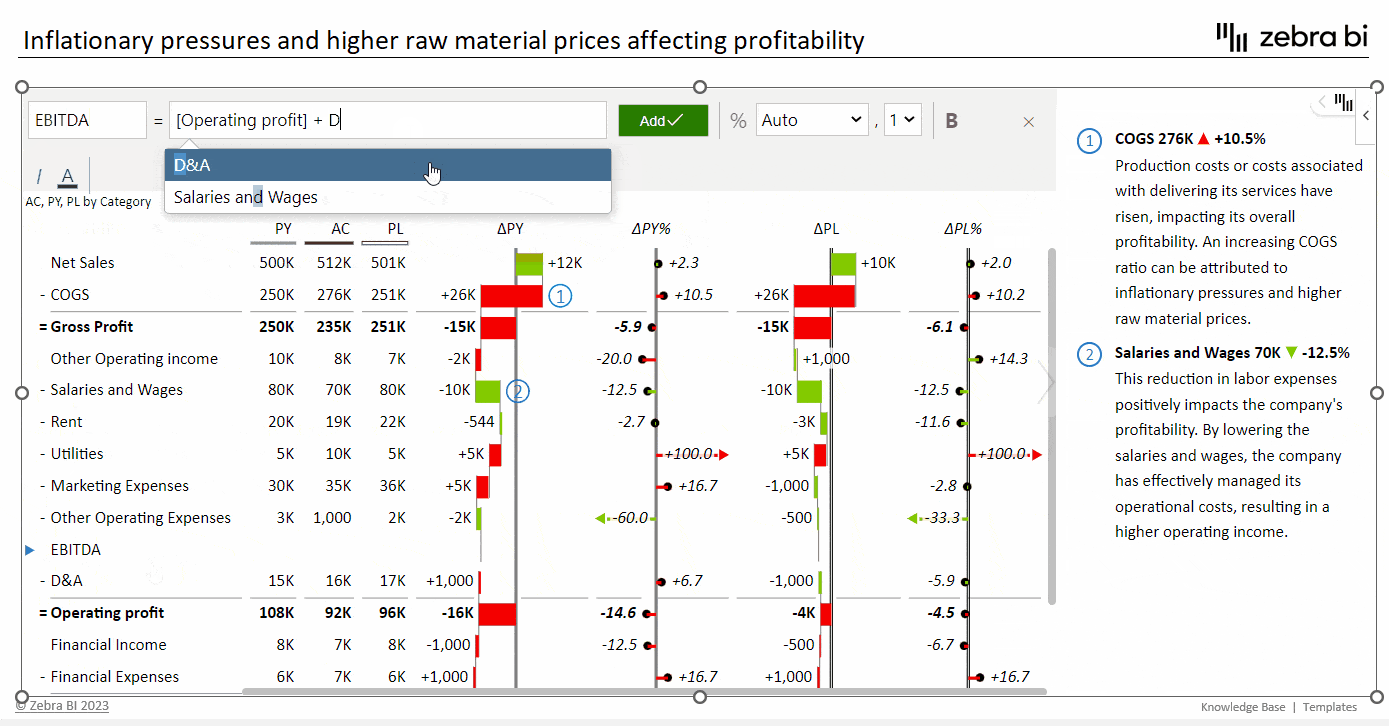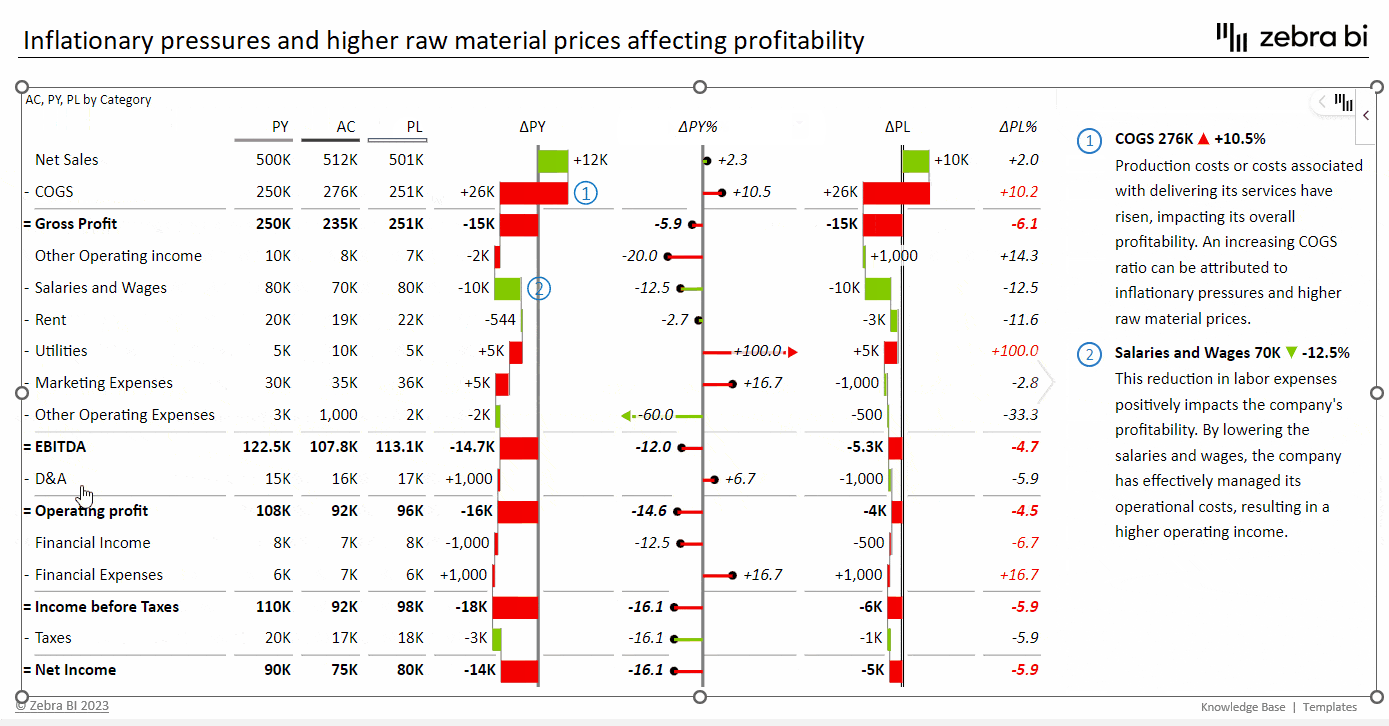
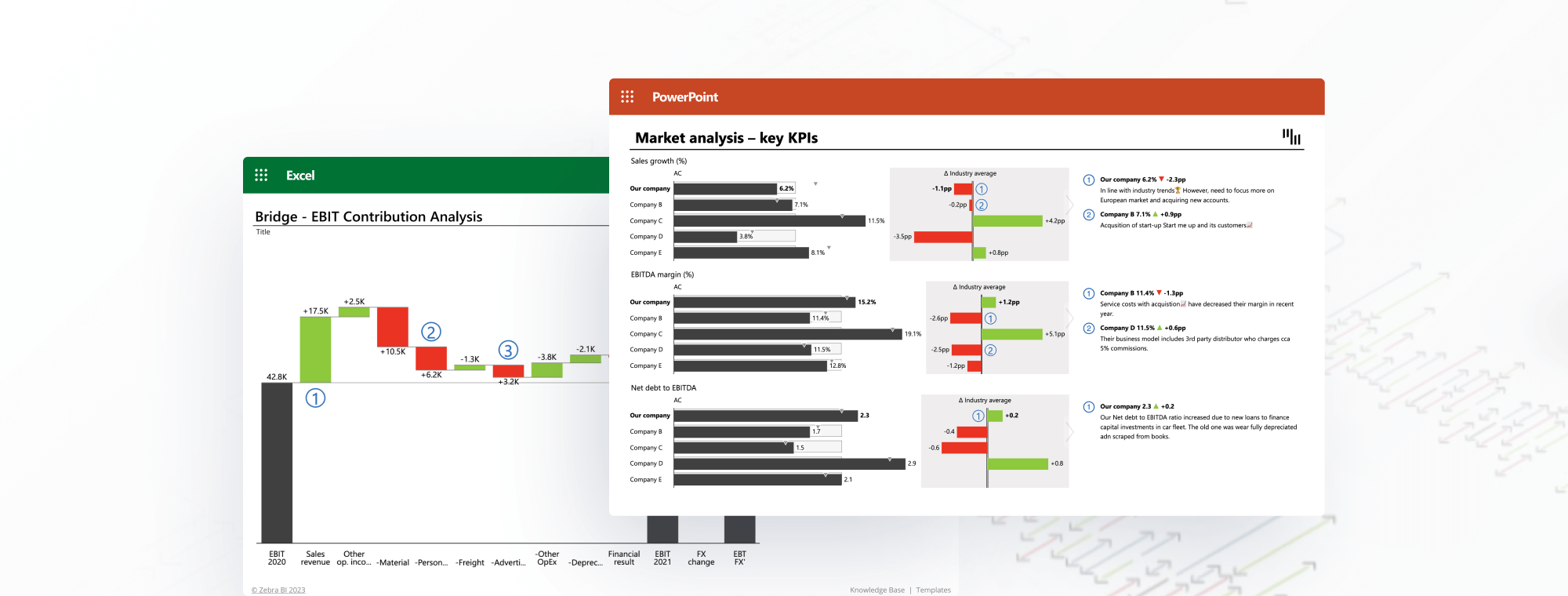
EBITDA Contribution Chart
EBITDA also serves as a vital tool in business valuation. Entrepreneurs and business valuators often use EBITDA to calculate a company’s valuation for a business sale or acquisition. A common method is to apply a multiple to EBITDA to determine company worth. An EBITDA contribution chart can be used to visually represent the EBITDA figure and its impact on the company's valuation.
EBITDA Drivers in a Waterfall Chart
EBITDA can also be presented using a waterfall chart, which visually displays the drivers contributing to EBITDA. This can help stakeholders understand the various factors that drive a company's EBITDA.
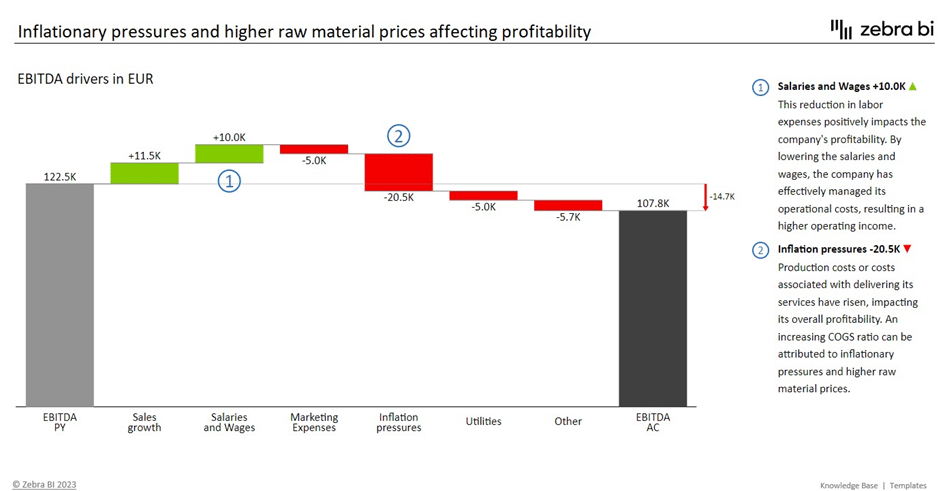
For further skill upgrade, we suggest reading PowerPoint Waterfall Charts: How To Create One That Doesn't Suck - Zebra BI
Benchmarking with EBITDA
EBITDA allows benchmarking by enabling comparisons between companies in different industries or with different financial structures. It helps evaluate a company's ability to generate profits from its primary business activities, regardless of external factors. This can be presented in a competitive analysis or market analysis chart. This will showcase how a company stands against its competitors in terms of EBITDA.
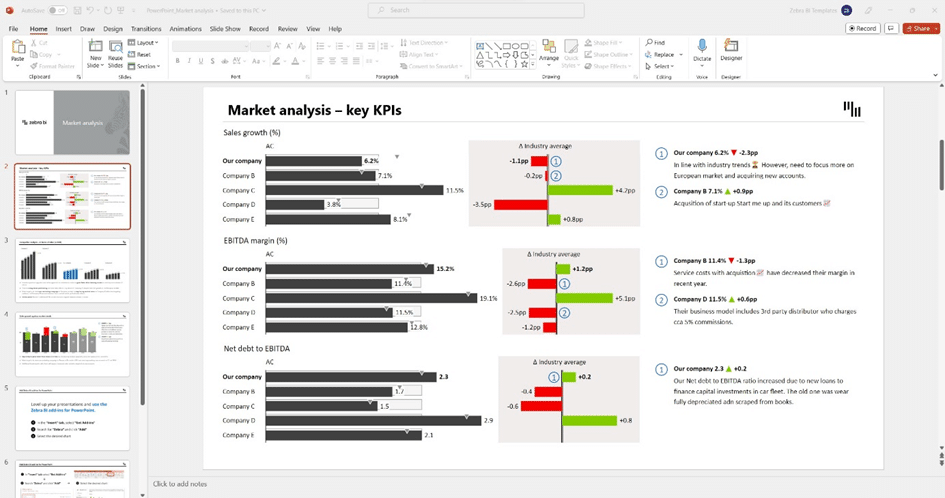
To sharpen your market analysis skills, consider reading How to use Excel for market analysis in 4 simple steps - Zebra BI
Presenting EBITDA in these various formats provides a multi-dimensional view of a company's financial standing. It allows for a deeper understanding of company operational profitability, facilitating more strategic decision-making.
Through these practical examples, it becomes clear that EBITDA is more than just a number. It's a lens through which businesses can assess their financial health, evaluate their performance, and guide their strategic decisions. Knowing how to calculate, interpret, and present EBITDA is an essential skill for any business professional, investor, or entrepreneur.
Conclusion
EBITDA serves as an invaluable tool in the financial landscape, offering a robust measure of operational profitability. As we've discovered, understanding what EBITDA is, how to calculate EBITDA, and how to effectively present it are crucial skills for anyone seeking to evaluate a company's financial health or guide strategic decision-making.
From business valuation to competitive benchmarking, EBITDA provides deep insights into a company's financial standing. It extends beyond net income to provide a clearer picture of a company's ability to generate cash profit from its core operations, disregarding the effects of financing decisions, accounting practices, or tax regulations.
Armed with this knowledge, you're now well-equipped to navigate financial analysis using EBITDA. Whether you're an investor assessing potential investment opportunities, a business professional evaluating your company's performance, or an entrepreneur preparing for an acquisition, understanding and applying EBITDA can enhance your financial acumen and inform your strategic decisions. With EBITDA in your financial toolkit, you're better prepared to make informed and strategic business decisions, propelling your success in the dynamic world of business.
Expand Your Financial Analysis Toolkit
Ready to delve further into EBITDA and enhance your financial analysis skills? Start your journey with Zebra BI for Office.

 September 8th
September 8th February 22nd
February 22nd